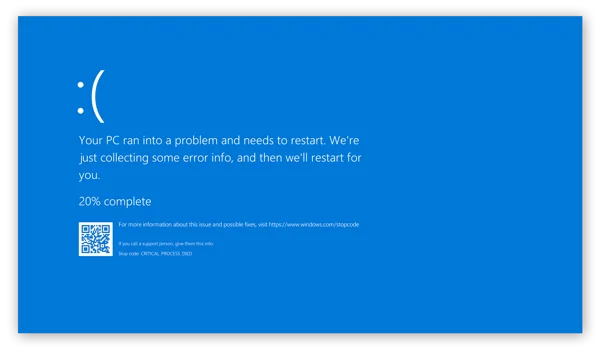
Step 1: Boot into Safe Mode
Safe Mode loads only essential programs, helping you troubleshoot easily.
-
Restart your PC.
-
Press F8 (or Shift + F8) during startup or force shutdown 3 times to trigger recovery mode.
-
Choose Troubleshoot → Advanced Options → Startup Settings → Restart → Safe Mode.
Pro Tip: If your PC runs fine in Safe Mode, the problem is likely a driver or software issue.
Step 2: Use the System File Checker (SFC)
Windows has a built-in tool to repair missing or corrupted system files.
-
Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
-
Type:
-
Press Enter and wait for the scan to complete. It will automatically fix any damaged files.
Step 3: Run the DISM Tool
If SFC alone doesn’t fix the issue, use DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management).
-
Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
-
Type the following commands one after another:
-
Press Enter after each command.
Pro Tip: This tool checks deeper and restores critical Windows system health.
Step 4: Perform a System Restore
If your system was working fine a few days ago, restore it to a previous point.
-
Search for System Restore in the Start menu.
-
Choose Recommended Restore or pick a different restore point when your PC was stable.
Step 5: Reset or Reinstall Windows (as a Last Resort)
If nothing works, you might need to reset your PC:
-
Go to Settings → Update & Security → Recovery.
-
Under Reset this PC, click Get started.
-
Choose whether to keep your files or remove everything.
(Backing up your data first is recommended!)
Quick Tips to Prevent Windows Corruption in the Future
-
Always update your Windows system and drivers.
-
Install reliable antivirus software.
-
Avoid sudden shutdowns or forced reboots.
-
Regularly back up your important files.